These are pons varolii cerebellum and medulla oblongata. These nerves control eye and eyelid movement.

Hindbrain Definition Function Structures Diagram Location Facts Britannica
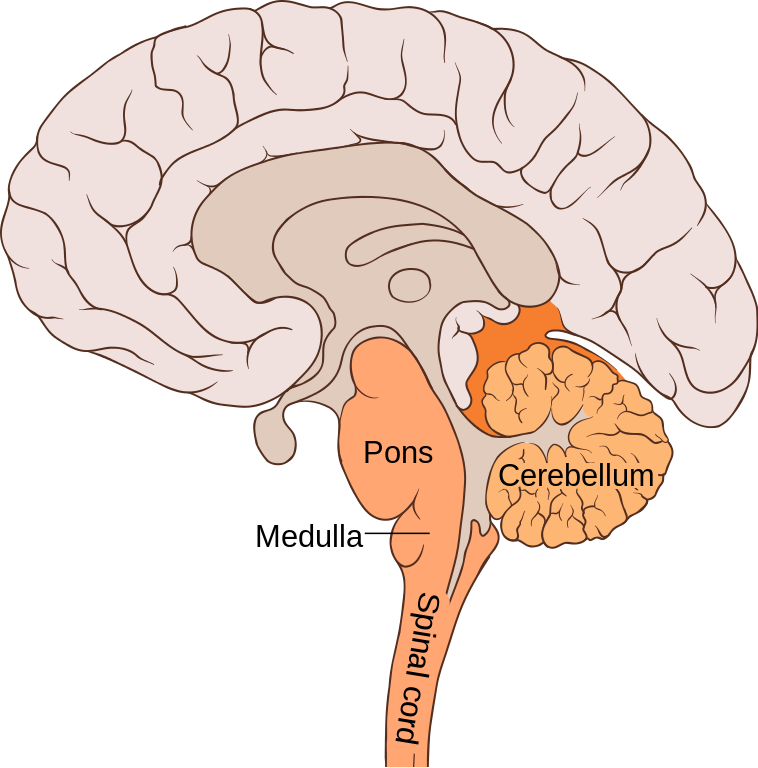
The pons cerebellum and medulla labeled.

. Identify the structural and functional subdivisions of the nervous system. The medulla is largely responsible for unconscious biological functions such as breathing heart and blood vessel activity swallowing vomiting sneezing and coughing. The midbrain regulates movement and aids in the processing of auditory and visual information.
The hindbrain contains several structures that regulate autonomic functions which are essential to survival and not under our conscious control. Brainstem The brainstem is a key. Its a fundamental part of the brain for information to go through from the prosencephalon to the bone marrow and vice versa.
Also known as the cerebral cortex the cerebrum is the largest part of the human brain and it is associated with higher brain function such as thought and. Identify the structures of the hindbrain midbrain and forebrain and describe their functions. Hindbrain also called rhombencephalon region of the developing vertebrate brain that is composed of the medulla oblongata the pons and the cerebellum.
The cerebellum Latin for little brain is a major feature of the hindbrain of all vertebratesAlthough usually smaller than the cerebrum in some animals such as the mormyrid fishes it may be as large as or even larger. Forebrain also known as the prosencephalon midbrain mesencephalon and hindbrain rhombencephalon. The forebrain is home to sensory processing endocrine structures.
HERE THE ANSWERS. The hindbrain works together to coordinate sleep patterns balance posture and motor activity and also regulates some unconscious but vital functions such as blood. Tink921 SHOW ANSWER The hindbrain is composed of the medulla the pons and the cerebellum.
Explore the parts of a neuron the definition of these nodes and discover their primary functions and structure. The anatomy of the brain is complex due its intricate structure and function. The hindbrain carries out several functions.
Identify the cranial nerves and describe their location and function. The medulla lies next to the spinal cord and controls functions outside conscious control such as breathing and blood flow. It includes most of the brainstem and a dense coral-shaped structure called the cerebellum.
These are the main and important parts of the hindbrain that are located in order to provide better control of the body and provide some other movement benefits. As mentioned the hindbrain is comprised of the pons medulla and cerebellar structures of your brain which together essentially act as the commander in charge of your automated systems talk. Its neurons play a.
The brainstem connects the spinal cordwith the cerebrum. The medulla lies next to the spinal cord and controls functions outside conscious control such as breathing and blood flow. Identify the basic regions of the hindbrain and describe their functions.
The three structures of the hindbrain are the medulla pons and cerebellum. The hindbrain developmentally derived from the rhombencephalon is one of the three major regions of our brains located at the lower back part of the brain. 4 Identify the structures that form part of the Hindbrain The hindbrain the.
The Hindbrain or rhombencephalon is located just above the spinal cord and is a developmental classification of parts of the vertebrae as part of the central nervous system. 4 Identify the structures that form part of the Hindbrain The hindbrain the from HPS 310 at Deakin University. The forebrain midbrain and hindbrain each with multiple parts.
The oculomotor and trochlear cranial nervesare located in the midbrain. Basically the RF allows people to ignore constant unchanging information such as the noise of an air. This amazing organ acts as a control center by receiving interpreting and directing sensory information throughout the body.
The three structures of the hindbrain are the medulla pons and cerebellum. Identify the structures of the hindbrain and describe their functions. The hindbrain coordinates functions that are fundamental to survival including respiratory rhythm motor activity sleep and.
210 Identify the different structures of the bottom part of the brain and describe the function of each. There are three major divisions of the brain. Forebrain Midbrain and Hindbrain.
The brain and spinal cord are the two main structures of the central nervous system. The pons connects the brainstem to the cerebellum and assists in coordination of movement sleep respiration appetite and facial. The hindbrain consists mainly of three parts that are important for the proper functioning of the body.
The midbrain can be divided into the dorsal or the upper half which is also known as the rectum and the tegmentum which is the bottom half of the brain. Download the Android app. The midbrain and hindbrain together compose the brainstem.
The medulla is largely responsible for unconscious biological functions such as breathing heart and blood vessel activity swallowing vomiting sneezing and coughing. The Structure And Function Of The Human Brain. Tink921 SHOW ANSWER The hindbrain is composed of the medulla the pons.
The brain structure is composed of three main parts. While there are a few different ways to divide the brain the developmental division roughly organizes the brain into three general regions. Identify the structures of the hindbrain and describe their functions.
These neurons are responsible for peoples ability to selectively attend to certain kinds of information in their surroundings. The hindbrain is made up of the medulla pons and cerebellum. The hindbrain is composed of the brainstem and the cerebellum and each structure is responsible for certain functions.
Brain Structure And Function Brain Injury British Columbia

Hindbrain Function Parts Structure What Is The Hindbrain Video Lesson Transcript Study Com
The Hindbrain Queensland Brain Institute University Of Queensland

Hindbrain Google Search Brain Anatomy And Function Brain Human Brain Anatomy
0 Comments